- Ethereum gas fees reach a five-year low due to Dencun upgrade and increased Layer 2 network activity.
- Lower transaction costs enhance user accessibility but slow the Ethereum token burning rate under EIP-1559.
Ethereum has seen its transaction fees, or gas fees, drop to a five-year low as of August 2024, reflecting increased efficiencies introduced by recent technological upgrades.
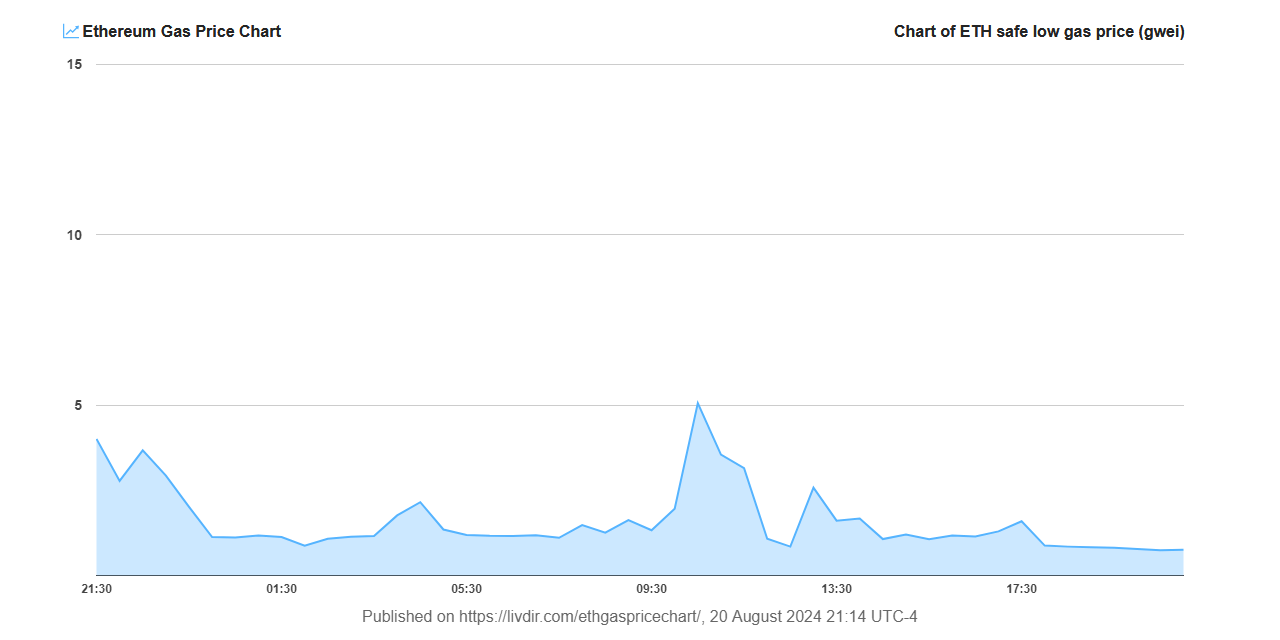
This decline in fees, while beneficial for user accessibility and cost, brings with it broader economic implications for the cryptocurrency’s cryptomarket.
Current #Ethereum (#ETH) safe low gas price: 0.829915657 Gwei
Fee chart(7d): https://t.co/OXRNccqoOB
24h: pic.twitter.com/TzgtKlxgyb— Ethereum Gas Price Chart🔔 (@ETHgasChart) August 20, 2024
The primary driver behind the reduced gas fees is the implementation of the Dencun upgrade in March 2024, which enhanced the capabilities of Layer 2 networks, thereby alleviating the burden on Ethereum’s main network.
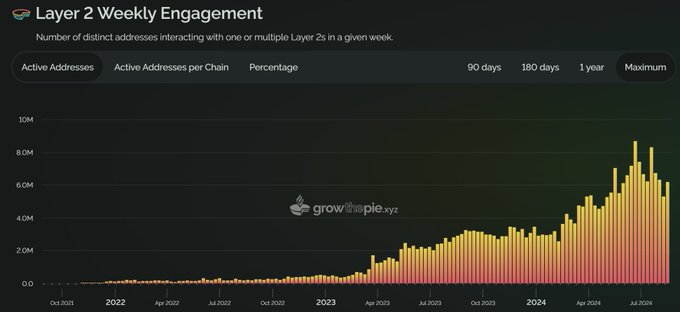
As reported in ETHNews, this technological enhancement not only lowered fees but also shifted much of the transactional load to these secondary layers.
An unintended consequence of these lower fees is a decrease in the rate of Ethereum tokens being burned. Ethereum’s EIP-1559 mechanism automatically burns a part of the transaction fees, which reduces the overall supply of Ethereum tokens in circulation.
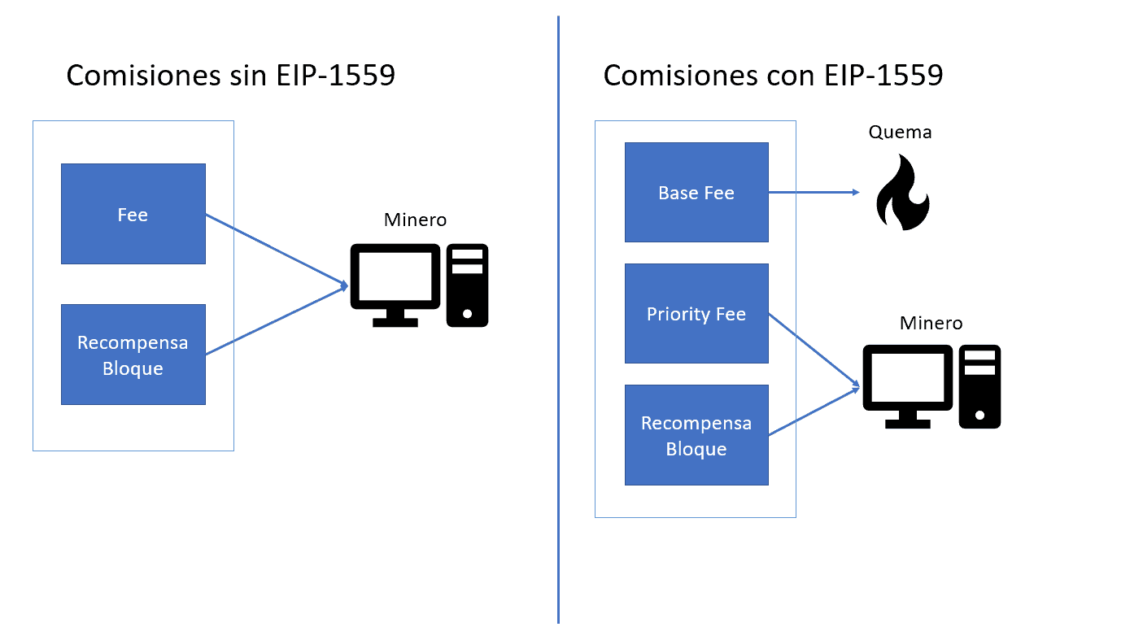
With the decrease in gas fees, the burning rate has slowed, leading to a less rapid decrease in the total token supply. From March to August 2024, Ethereum’s supply saw a marginal increase from 120 million to 120.2 million tokens.
[mcrypto id=”12523″]
While an increase in token supply could potentially enhance liquidity and encourage broader use of Ethereum, it may also exert downward pressure on its price.
Market analysis by ETHNews reveals that Ethereum has struggled to surpass the $3,000 mark, a key psychological and technical resistance level.
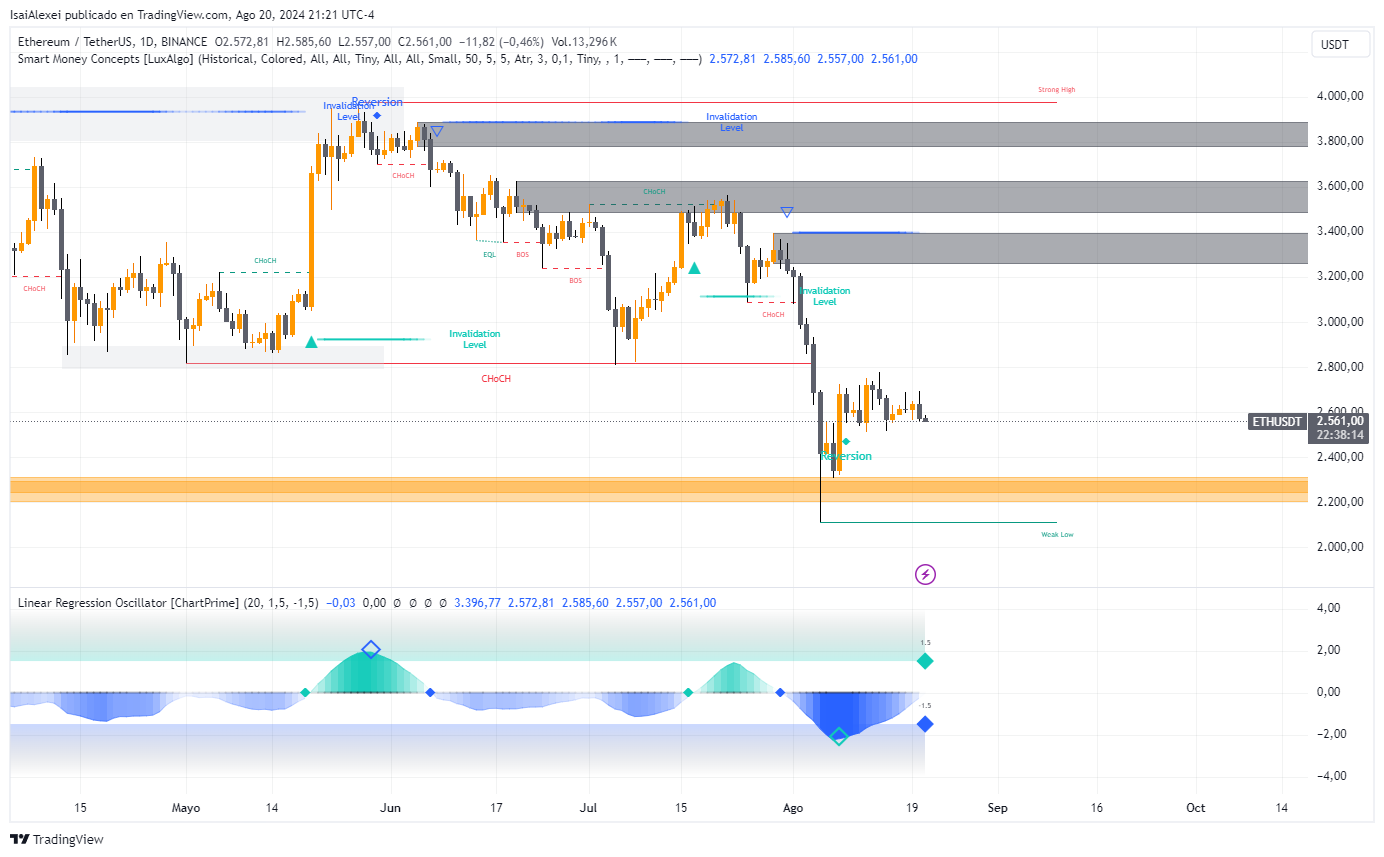
For the first time ever, the ETH balance on exchanges has dropped below 10%.
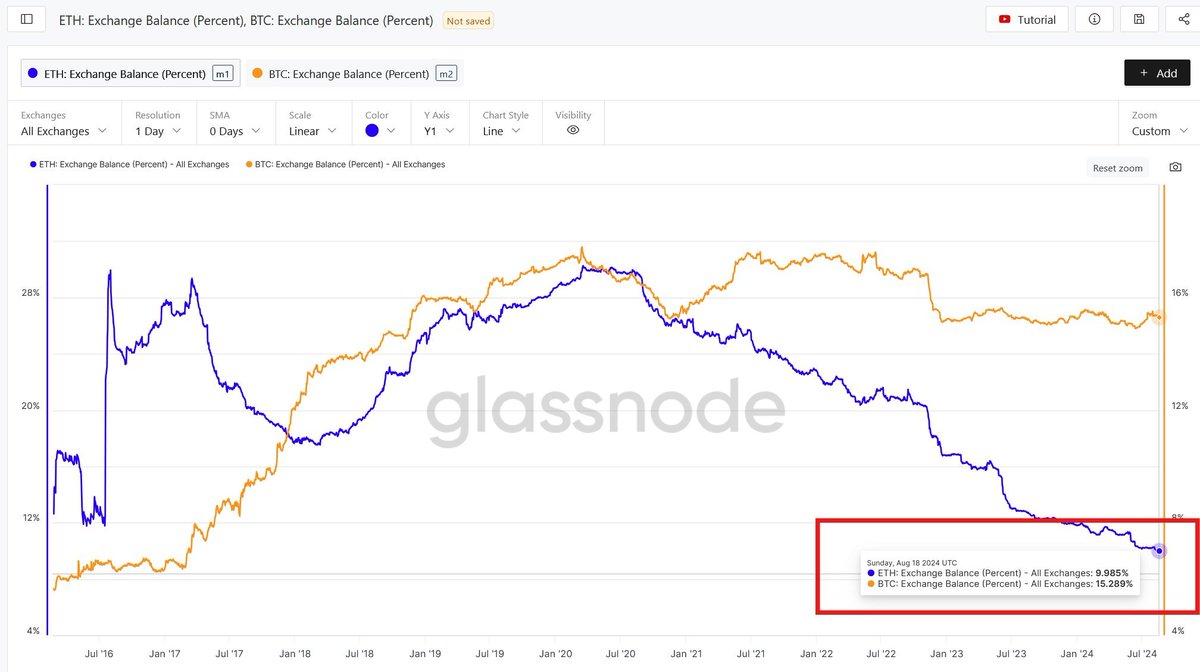
This struggle is evident in the cryptocurrency’s price movements and is underscored by market sentiment indicators such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI), which, at around 40, indicates a bearish trend.
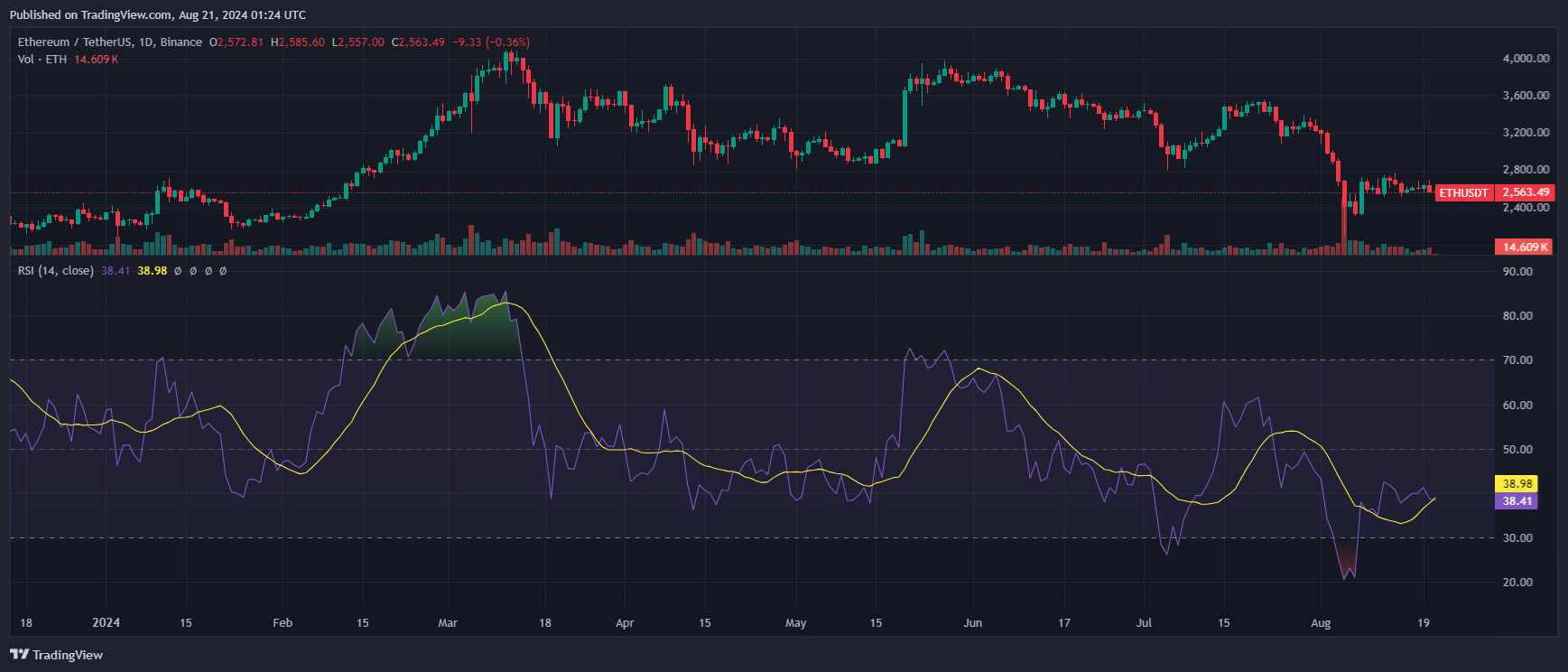
This nuanced scenario presents a complex interplay between technological advancements and market economics.
While the reduction in gas fees marks a technological success, making the platform more accessible, it also introduces challenges to Ethereum’s economic model by slowing the reduction of supply, potentially impacting its price appreciation in the short term.



